Last updated on November 16th, 2025 at 08:31 am
Have you ever struggled to express your thoughts clearly in a conversation? Or admire someone who can effortlessly capture an audience’s attention with their words? The secret to effective communication lies not just in what you say, but in how you say it. Oral communication examples are all around us from casual conversations with friends to delivering high-stakes presentations at work.
This guide will explore the importance of oral communication, the different types, practical oral communication examples, and how you can improve your skills.
Key Characteristics of Oral Communication
- Spoken Words: The primary mode of communication is through speech.
- Non-Verbal Cues: Tone, body language, facial expressions, and gestures enhance the message.
- Interactive: Involves feedback and dialogue.
Why is Oral Communication Important?
- Building Relationships: Communication is the foundation of any relationship—personal or professional. The better you communicate, the stronger the bonds you form. According to the International Association of Business Communicators, effective oral communication examples can lead to a 47% increase in employee engagement.
- Influencing Others: Oral communication allows you to persuade, inspire, and motivate others. As Dale Carnegie said, “You can make more friends in two months by becoming interested in other people than in two years by trying to get other people interested in you.”
- Collaboration and Teamwork: In group settings, effective communication ensures that everyone understands the goals and objectives. Strong oral communication examples indicate that teams with good communication skills are 25% more productive.
- Career Advancement: A National Association of Colleges and Employers survey found that 80% of employers value oral communication skills, making mastery of these skills a powerful asset in your career.
- Conflict Resolution: Whether in personal or professional settings, clear communication often demonstrated through oral communication examples—is key to resolving misunderstandings and conflicts.
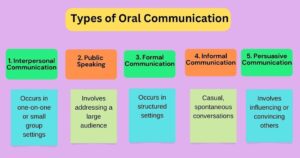
Types of Oral Communication
1. Interpersonal Communication
Occurs in one-on-one or small group settings: These include casual conversations, team discussions, or informal chats with colleagues. Effective interpersonal oral communication examples can strengthen workplace relationships.
2. Public Speaking
Involves addressing a large audience: Such as in seminars, conferences, or workshops. This requires strong presentation skills and the ability to engage and connect with an audience. Great speakers often use oral communication examples to illustrate their points.
3. Formal Communication
Occurs in structured settings: Like meetings, presentations, or interviews. These require careful preparation and clarity, often highlighted by specific oral communication examples.
4. Informal Communication
Casual, spontaneous conversations: These happen in social settings, such as talking with friends or chatting informally at the workplace. Informal oral communication examples can enhance team dynamics.
5. Persuasive Communication
Involves influencing or convincing others: To adopt a certain point of view, such as in sales pitches or debates. Persuasive oral communication examples can be very effective in marketing and advocacy.
Examples of Oral Communication
1. Explaining a Work-Related Project:
Imagine you are leading a project team. You might organize a meeting where you present the project’s objectives, timelines, and responsibilities. During your presentation, you explain complex concepts using clear language, supported by visual aids like slides. This ensures that everyone understands their roles and expectations.
 |
| 15 Powerful Oral Communication Examples You Need to Know |
2. Participating in a Group Discussion:
For example, you might say, “I think we should consider a new marketing strategy. What are your thoughts on these oral communication examples?”
3. Giving a Speech to an Audience:
This approach draws the audience’s attention and sets the stage for your main points.
4. Conducting a Job Interview:
5. Explaining Technical Concepts:
For example, “Think of our network like a highway—data travels along these routes, and sometimes there are traffic jams when too many users are online. Here’s how we can alleviate that…” This analogy simplifies technical jargon and provides oral communication examples that make it accessible to everyone.
6. Presenting Research Findings:
You might say, “Our study found that 75% of participants preferred the new method over the traditional one.” Using statistics and oral communication examples helps convey your message effectively.
7. Conflict Resolution:
8. Networking at Events:
This initiates meaningful conversations and establishes connections, showcasing effective oral communication examples.
9. Facilitating a Workshop:
This encourages participation and empowers attendees to share their experiences, providing practical oral communication examples.
10. Conducting a Training Session:
This interactive approach fosters an engaging learning environment, filled with essential oral communication examples.
11. Leading a Virtual Meeting
This interaction highlights the importance of engaging directly with your audience through modern communication channels.
13. Engaging in Customer Service
14. Conducting Exit Interviews
This encourages honest dialogue and helps organizations learn from departing employees.
15. Hosting a Podcast
Tips for Effective Oral Communication
Know Your Audience:
Tailor your message to the audience’s level of knowledge and interest. Whether you are speaking to a child or a professional, adjusting your language is key to effective communication.
Prepare and Practice:
Preparation is critical. Whether you are speaking informally or giving a presentation, practicing your delivery will make you more confident and effective.
Speak Clearly and Confidently:
Enunciate your words, maintain a moderate pace, and use a confident tone. Good vocal delivery is essential for getting your message across.
Use Non-Verbal Cues:
Body language, gestures, and facial expressions complement what you say. Maintain good posture, make eye contact, and avoid fidgeting.
Listen Actively:
Communication is a two-way process. Listen attentively to others, ask questions, and provide feedback.
Be Concise:
Avoid rambling. Stick to the main points to ensure your audience stays engaged and the message is clear.
Seek Feedback:
Ask others for constructive feedback on your communication style and areas for improvement.
Practice Regularly:
The more you communicate, the better you become. Whether through casual conversations or public speaking opportunities, practice is key.
Leverage Storytelling:
Use storytelling to make your message relatable and memorable. A well-told story captures attention and helps your audience connect emotionally with your ideas.
Adapt to Real-Time Feedback:
Pay attention to your audience’s reactions, such as body language or verbal cues, and adjust your delivery accordingly. For instance, slow down if they seem confused or elaborate on points where they show interest.
 |
| 15 Powerful Oral Communication Examples You Need to Know |
Want to Master Oral Communication Even Faster?
Join millions of confident speakers worldwide. Toastmasters International’s Public Speaking Tips offer free guides, videos, and proven techniques used by top leaders to speak with clarity and impact.
Key Takeaways
- Oral communication involves both speaking and listening and is vital for building relationships, resolving conflicts, and achieving goals.
- Effective communication skills are highly valued by employers, with 80% of employers citing them as essential when hiring.
- Regular practice, preparation, and active listening are key to mastering oral communication.